2019-2023 Global new PV equivalent annual emissions reduction of 1.1 billion tons, the largest contribution from China
2024/03/18
From 2022 to 2023, global solar PV capacity additions increased by more than 80% to a record 420 GW. In China, despite the phasing out of government subsidies for utility, commercial and industrial-scale PV projects, new solar PV installations grew 2.5 times, accounting for an unprecedented 62% of new global additions. Since December 2022, the rapid expansion of China's photovoltaic manufacturing industry has reduced the cost of photovoltaic modules by 50%, improving the competitiveness of solar PV.
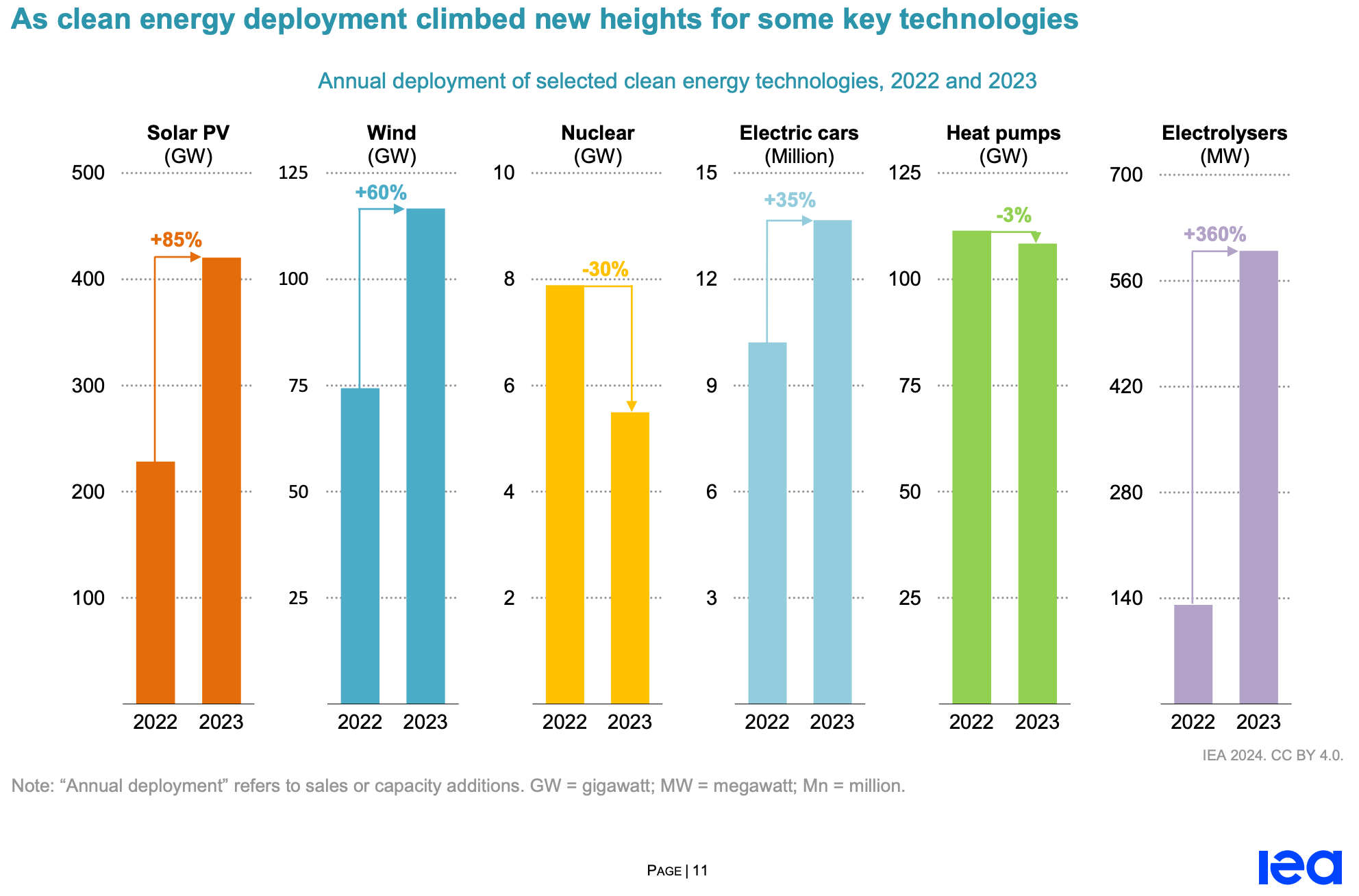
In the European Union, new PV installations rose by a quarter last year to a record 53 gigawatts. This is because after the beginning of the Russia-Ukraine war, EU member states improved the policy environment to accelerate the deployment of renewable energy in order to reduce gas consumption. This has almost doubled the number of new solar PV installations since 2021. High retail electricity prices as a result of the energy crisis have also prompted more consumers to install solar photovoltaic panels on their roofs to reduce their energy bills. In the United States, with the easing of supply chain issues that led to a decline in new installations in 2022, coupled with federal tax incentives and state-level support continuing to drive utility-scale and rooftop solar PV applications, new PV installations in the United States in 2023 increased by 50% year-over-year to 32 GW of new capacity.
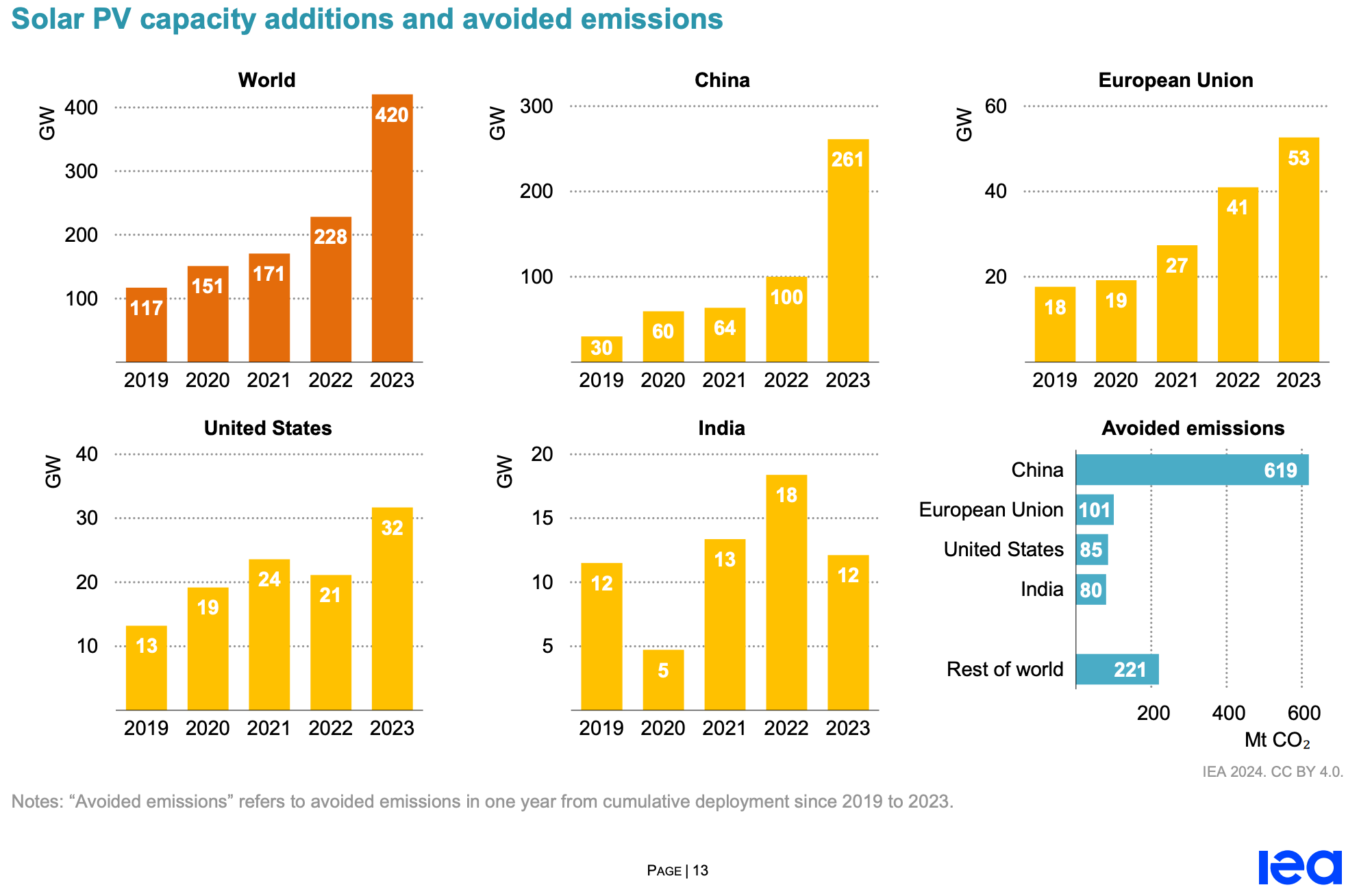
In 2023, India added 12 GW of new solar PV installations, a third less than in 2022. This is due to lower competitive tenders for utility-scale solar projects in previous years, coupled with supply chain issues. In Brazil, driven by a net metering program to stimulate rooftop solar PV, installations grew by more than 20 percent year-on-year and new capacity was added more than in India.
Globally, new solar PV generation between 2019 and 2023 will reduce CO2 emissions by about 1.1 billion tonnes per year, equivalent to Japan's total annual emissions. By far the biggest contributor to emissions reductions was China, which avoided more than 600 million tonnes of solar PV additions. In Australia and New Zealand, new solar PV generation from 2019 to 2023 averted the equivalent of 10% of the region's total annual energy emissions in 2023.
Source: International Energy Small Data

